tsconfig.json配置讲解
关于 tsconfig.json 的相关详细配置参考官方文档说明:https://www.typescriptlang.org/tsconfig/#Type_Checking_6248
一、tsconfig.json配置
如果一个目录下存在一个 tsconfig.json 文件,那么它意味着这个目录是 TypeScript 项目的根目录。 tsconfig.json 文件中指定了用来编译这个项目的根文件和编译选项。 一个项目可以通过以下方式之一来编译:
不带任何输入文件的情况下调用
tsc命令,编译器会从当前目录开始去查找 tsconfig.json 文件,逐级向上搜索父目录。不带任何输入文件的情况下调用
tsc,且使用命令行参数--project(或-p)指定一个包含 tsconfig.json 文件的目录。当命令行上指定了输入文件时,tsconfig.json 文件会被忽略。
1.1、files 字段
"files"指定一个包含相对或绝对文件路径的列表
🔔注意:只能文件,不能是文件夹
1.2、include
include 字段用于指明需要被 tsc 编译的文件或文件夹列表,例如
{
"include": ["src", "global.d.ts"]
}1.3、exclude
exclude 字段用于排除不需要 tsc 编译的文件或文件夹列表,例如:
{
"exclude": ["test.ts", "src/test.ts"],
}1.4、include和exclude的细节
"include" 和 "exclude" 属性指定一个文件 glob 匹配模式列表。 支持的 glob 通配符有
*匹配0或多个字符(不包括目录分隔符)?匹配一个任意字符(不包括目录分隔符)**/递归匹配任意子目录
如果一个 glob 模式里的某部分只包含
*或.*,那么仅有支持的文件扩展名类型被包含在内(比如默认 .ts,.tsx,和 .d.ts, 如果 allowJs 设置能 true 还包含 .js 和 .jsx )如果
"files"和"include"都没有被指定,编译器默认包含当前目录和子目录下所有的 TypeScript 文件(.ts,.d.ts和.tsx),排除在"exclude"里指定的文件。JS文件(.js和.jsx)也被包含进来如果allowJs被设置成true。 如果指定了"files"或"include",编译器会将它们结合一并包含进来。 使用"outDir"指定的目录下的文件永远会被编译器排除,除非你明确地使用"files"将其包含进来(这时就算用exclude指定也没用)使用
"include"引入的文件可以使用"exclude"属性过滤。 然而,通过"files"属性明确指定的文件却总是会被包含在内,不管"exclude"如何设置。 如果没有特殊指定,"exclude"默认情况下会排除node_modules,bower_components,jspm_packages和<outDir>目录任何被
"files"或"include"指定的文件所引用的文件也会被包含进来。A.ts引用了B.ts,因此B.ts不能被排除,除非引用它的A.ts在"exclude"列表中。tsconfig.json文件可以是个空文件,那么所有默认的文件(如上面所述)都会以默认配置选项编译。
1.5、extends
tsconfig.json 文件可以利用 extends 属性从另一个配置文件里继承配置。
extends 是 tsconfig.json 文件里的顶级属性(与 compilerOptions,files,include,和 exclude 一样)。 extends 的值是一个字符串,包含指向另一个要继承文件的路径。
1.6、compileOnSave
compileOnSave 是声明是否需要在保存时候自动触发 tsc 编译的字段,一般来说,我们的代码编译过程会通过 Rollup、Webpack 等打包构建工具,并且使用热更新,因此无需配置该项,保持缺省即可。
{
"compileOnSave": false,
}1.7、compilerOptions
compilerOptions 为编译选项,详细可以参考下一章
二、compilerOptions选项详解
2.1、类型检查相关配置
2.1.1、strict
当 strict 为 true 时,会默认开启一系列相关类型检查行为。相互关联的配置项有
alwaysStrictstrictNullChecksstrictBindCallApplystrictBuiltinIteratorReturnstrictFunctionTypesstrictPropertyInitializationnoImplicitAnynoImplicitThisuseUnknownInCatchVariables
如果需要关闭单个配置,就单独设置该项为 false 即可,例如
"compilerOptions": {
// 类型检查相关配置
"strict": true
"alwaysStrict": false
},2.1.2、alwaysStrict
alwaysStrict 选项告诉 TypeScript 编译器以严格模式解析所有源代码,并为每个生成的 JavaScript 文件在顶部添加 "use strict"; 指令
示例代码
function example() {
// 在严格模式下,这会导致编译错误
undeclaredVar = "hello"; // 错误:找不到名称 'undeclaredVar'
// 在严格模式下,这会导致编译错误
const obj = { x: 1 };
with (obj) { // 错误:严格模式禁止使用 'with' 语句
console.log(x);
}
}
example();会被编译成
"use strict";
function example() {
// 在严格模式下,这会导致运行时错误
undeclaredVar = "hello"; // ReferenceError: undeclaredVar is not defined
}
example();2.1.3、strictNullChecks
当 strictNullChecks 为 false 时,语言实际上忽略了 null 和 undefined。这可能会导致运行时出现意外错误。
当 strictNullChecks 为 true 时,null 和 undefined 有自己的不同类型,如果您尝试在需要具体值的地方使用它们,您将收到类型错误。
例如:以下代码中的 users.find 不能保证它真的会找到一个用户,但你可以编写代码
declare const loggedInUsername: string;
const users = [
{ name: 'Oby', age: 12 },
{ name: 'Heera', age: 32 },
];
const loggedInUser = users.find((u) => u.name === loggedInUsername);
console.log(loggedInUser.age);将 strictNullChecks 设置为 true 将引发一个错误,表明您在尝试使用它之前尚未保证 loggedInUser 存在。
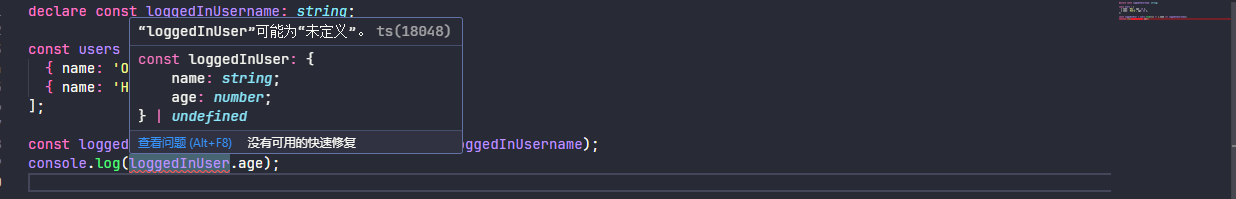
将 strictNullChecks 设置为 false 时则不会提示,可能会导致运行时出现意外错误。
2.1.4、strictBindCallApply
设置后,TypeScript 将检查函数 call、bind 和 apply 的内置方法是否使用底层函数的正确参数调用,示例如下
function fn(x: string) {
return parseInt(x);
}
const n1 = fn.call(undefined, "10");
const n2 = fn.call(undefined, false);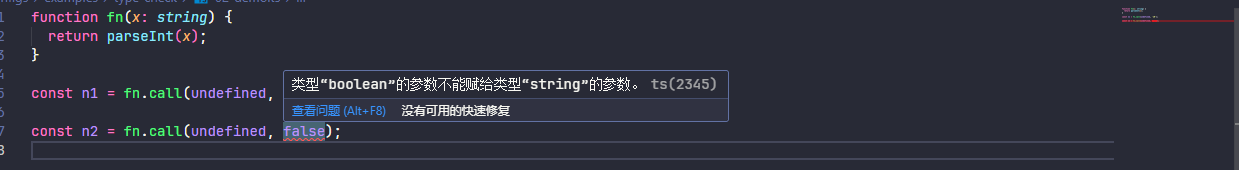
2.1.5、strictBuiltinIteratorReturn
const array = [1, 2, 3];
const iterator = array[Symbol.iterator]();
// 正常迭代
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }
// 调用 return 方法用于提前终止迭代 - 这里类型检查不够严格
const result = iterator.return(); // error
console.log(result); // { value: undefined, done: true }2.1.6、strictFunctionTypes
function fn(x: string) {
console.log('Hello, ' + x.toLowerCase());
}
type StringOrNumberFunc = (ns: string | number) => void;
/**
* 不能将类型“{ (x: string): number; (x: string): void; (x: string): void; }”分配给类型“StringOrNumberFunc”。
参数“x”和“ns” 的类型不兼容。
不能将类型“string | number”分配给类型“string”。
不能将类型“number”分配给类型“string”。
*/
let func: StringOrNumberFunc = fn; // error
func(10);
/**
* 当 strictFunctionTypes 启用时
* 上述写法可以改成以下写法
*/
type Methodish = {
func(x: string | number): void;
};
function fn(x: string) {
console.log('Hello, ' + x.toLowerCase());
}
// Ultimately an unsafe assignment, but not detected
const m: Methodish = {
func: fn,
};
m.func(10);2.1.7、strictPropertyInitialization
当设置为 true 时,当类属性已声明但未在构造函数中设置时,TypeScript 将引发错误。
class UserAccount {
name: string;
accountType = 'user';
email: string;
address: string | undefined;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
// Note that this.email is not set
}
}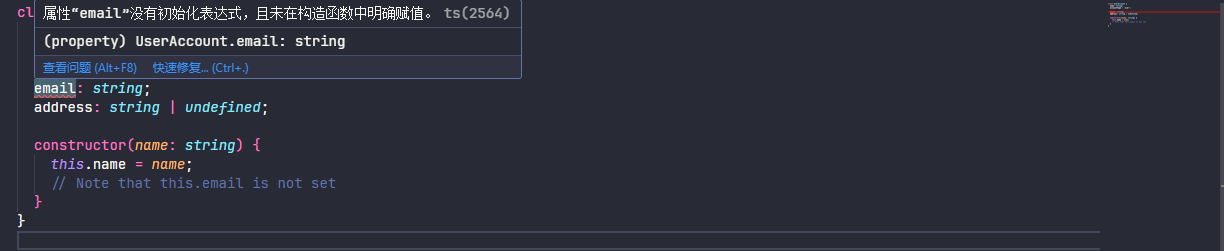
上述的情况 name 和 email 是必填的,所以需要在 constructor 中进行设置
2.1.8、noImplicitAny
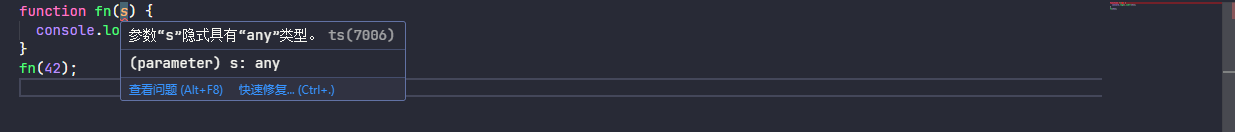
在某些情况下,如果不存在类型注释,当它无法推断该类型时,TypeScript 将回退到变量的 any 类型。
function fn(s) {
console.log(s.subtr(3));
}
fn(42);上述代码并没有什么错误,当 noImplicitAny 设置为 true 时就会提示 s 参数类型为隐式 any
2.1.9、noImplicitThis
在隐含 “any” 类型的 “this” 表达式上引发错误,示例如下
class Rectangle {
width: number;
height: number;
constructor(width: number, height: number) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
getAreaFunction() {
return function () {
return this.width * this.height;
};
}
}下面的类返回一个尝试访问 this.width 和 this.height 的函数,但 getAreaFunction 内部 函数中的上下文 不是 Rectangle 的实例

2.1.10、useUnknownInCatchVariables
在 TypeScript 4.0 中,添加了支持以允许将 catch 子句中变量的类型从 any 更改为 unknown。允许以下代码:
try {
// ...
} catch (err: unknown) {
// We have to verify err is an
// error before using it as one.
if (err instanceof Error) {
console.log(err.message);
}
}2.1.11、allowUnreachableCode
allowUnreachableCode 表示是否允许无法访问的代码,为 true 时表示忽略,false 时引发有关无法访问代码的编译器错误,默认为 undefined 向编辑者提供建议作为警告
示例如下
function fn(n: number) {
if (n > 5) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
return true;
}其中函数内的最后一行执行代码 return true; 代码始终无法执行到该行代码
2.1.12、allowUnusedLabels
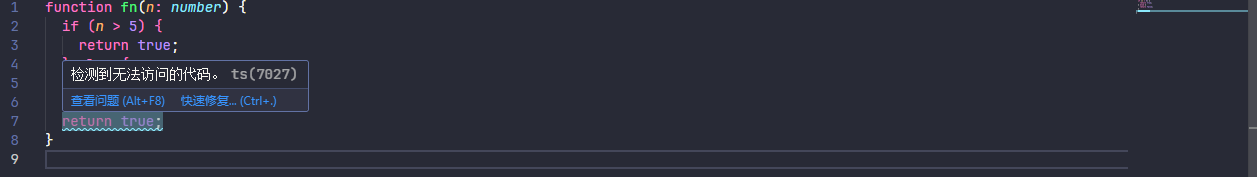
allowUnusedLabels 表示是否允许未使用的标签,为 true 时表示忽略,false 时引发有关无法访问代码的编译器错误,默认为 undefined 向编辑者提供建议作为警告
首先需要先介绍以下 label 语法,JavaScript 是存在 label 语法的,像以下示例一样
function exampleWithUnusedLabel() {
unusedLabel: for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
}
function anotherExample() {
myLabel: {
console.log("This is a block");
}
}像上述中的 exampleWithUnusedLabel 和 myLabel 表示其中的代码块含义,更加详细的了解可自行参考其他文档深入了解,这里不做详细描述。
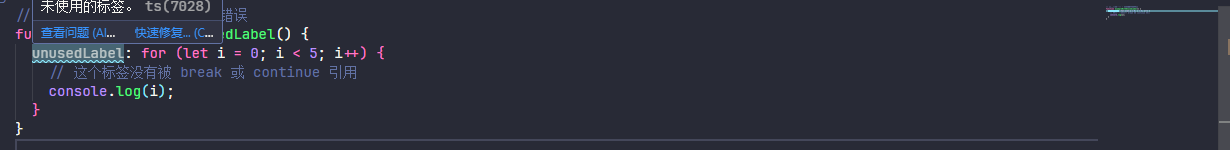
像这里设置 allowUnusedLabels 为 false 时就会提示,exampleWithUnusedLabel 并未被其他地方引用
2.1.13、exactOptionalPropertyTypes
exactOptionalPropertyTypes 选项让 TypeScript 对可选属性进行更严格的检查。启用后,可选属性只能被省略或赋值为明确类型,不能显式赋值为 undefined。
interface User {
name: string;
age?: number;
}
const user1: User = { name: 'Alice' }; // 省略 optional
const user2: User = { name: 'Jack', age: 42 }; // 赋值为 number
// 当 exactOptionalPropertyTypes 为 false 时是允许的,为 true 则会提示错误
const user3: User = { name: 'black', age: undefined }; // 赋值为 undefined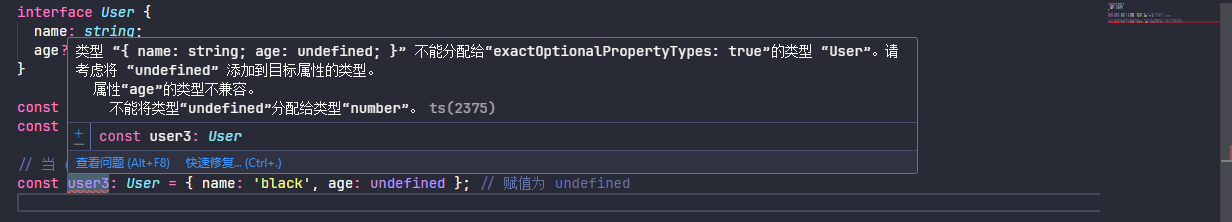
2.1.14、noFallthroughCasesInSwitch
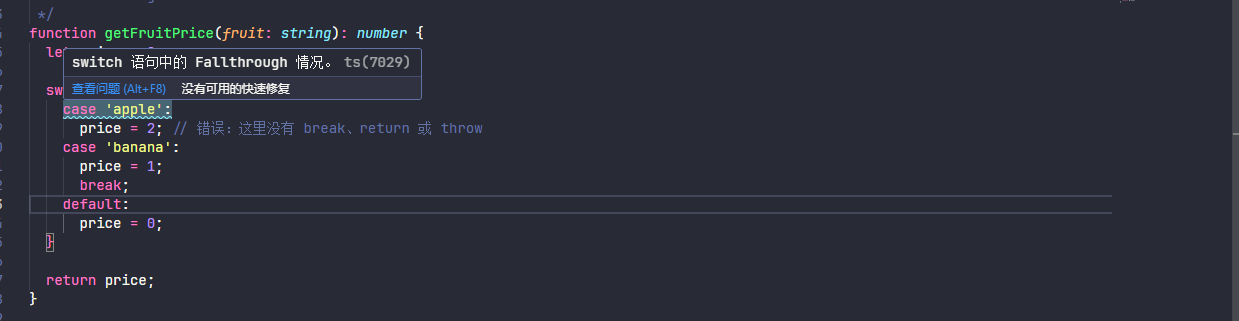
noFallthroughCasesInSwitch 选项用于防止在 switch 语句中出现意外的 case 穿透(fallthrough)行为。当启用时(推荐),TypeScript 会检查每个 case 块是否以 break、return 或 throw 等语句结束,如果没有,就会报错。设置为 true 表示开启,false 为关闭。示例如下
function getFruitPrice(fruit: string): number {
let price = 0;
switch (fruit) {
case 'apple':
price = 2; // 错误:这里没有 break、return 或 throw
case 'banana':
price = 1;
break;
default:
price = 0;
}
return price;
}
2.1.15、noImplicitOverride
当使用继承类时,子类可能会覆盖基类中的方法,覆盖方法前需要加 override 修饰符,示例如下
class Album {
download() {
// Default behavior
}
}
class SharedAlbum extends Album {
download() {
// Override to get info from many sources
}
}当 noImplicitOverride 设置为 true 时(默认为 false),会提示以下错误
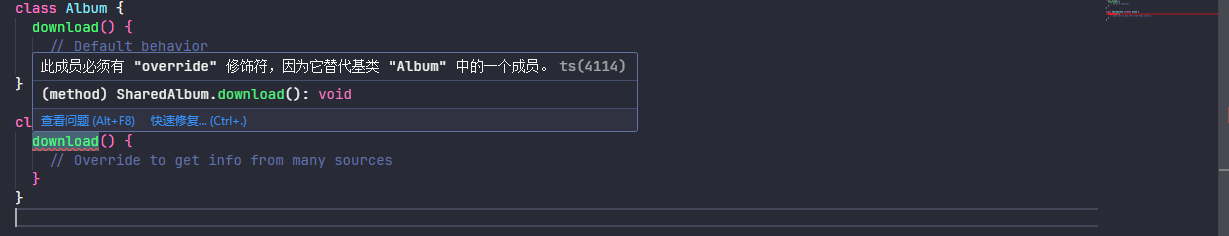
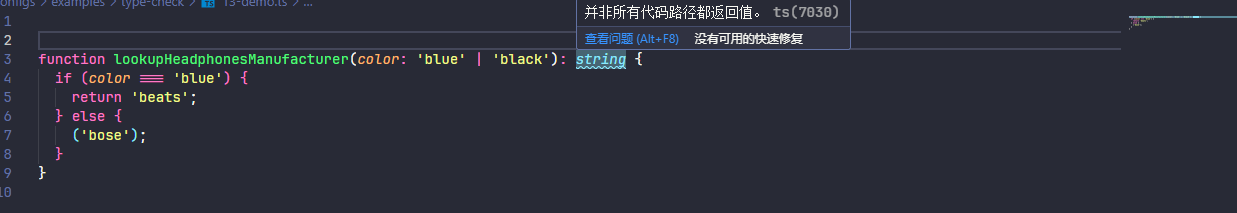
2.1.16、noImplicitReturns
启用后,TypeScript 将检查函数中的所有代码路径,以确保它们返回值
function lookupHeadphonesManufacturer(color: 'blue' | 'black'): string {
if (color === 'blue') {
return 'beats';
} else {
('bose');
}
}
2.1.17、noUncheckedIndexedAccess
noUncheckedIndexedAccess 选项让 TypeScript 对数组和索引签名属性的访问更加严格。启用后,通过索引访问数组元素或对象动态属性时,返回的类型会包含 undefined,强制你处理可能不存在的值。示例如下
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const first = numbers[0];
const tenth = numbers[9];当 noUncheckedIndexedAccess 为 false 不启用时
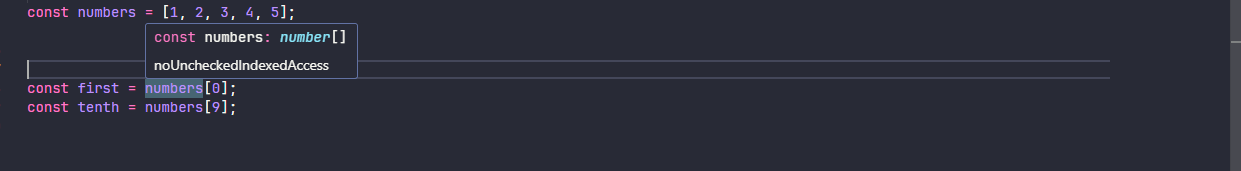
当 noUncheckedIndexedAccess 为 true 启用时
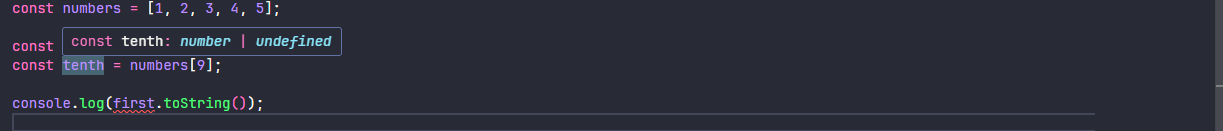
2.1.18、noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature
noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature 选项当访问已知属性使用 . 符号,访问索引属性使用方括号 [] 进行访问。这样可以更清楚地区分已知属性和动态属性。示例如下
interface Config {
// 已知属性
timeout: number;
retries: number;
// 索引签名(动态属性)
[key: string]: number;
}
const config: Config = {
timeout: 1000,
retries: 3,
customDelay: 500, // 动态属性
};
console.log(config.timeout); // ✅ 1000 - 点符号访问已知属性
console.log(config['timeout']); // ✅ 1000 - 方括号访问已知属性
console.log(config.customDelay); // ✅ 500 - 点符号访问动态属性(但有问题!)
console.log(config['customDelay']); // ✅ 500 - 方括号访问动态属性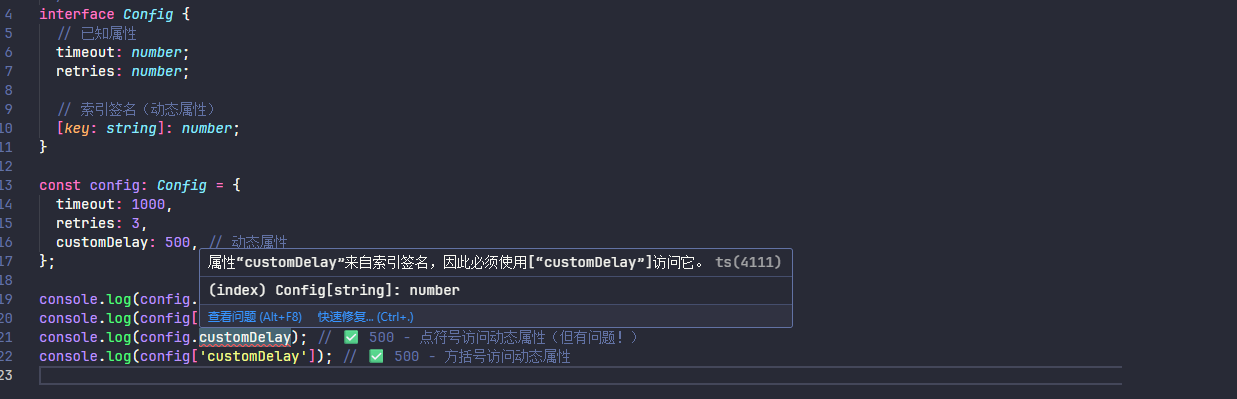
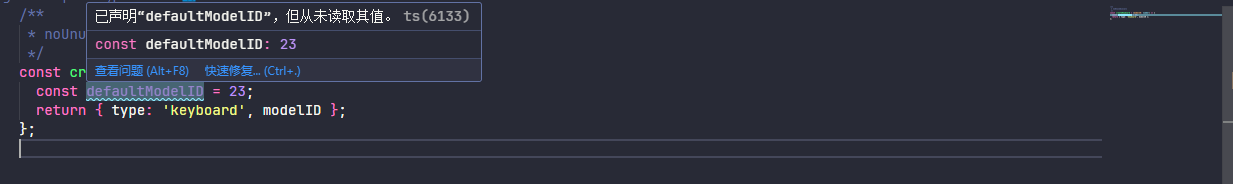
2.1.19、noUnusedLocals
报告未使用的局部变量的错误,为 true 时启用,false 为关闭
const createKeyboard = (modelID: number) => {
const defaultModelID = 23;
return { type: 'keyboard', modelID };
};
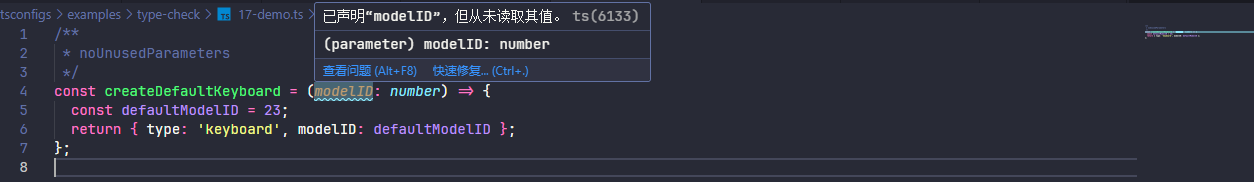
2.1.20、noUnusedParameters
报告函数中未使用参数的错误,为 true 时启用,false 为关闭
const createDefaultKeyboard = (modelID: number) => {
const defaultModelID = 23;
return { type: 'keyboard', modelID: defaultModelID };
};
2.1.21、类型检查总结
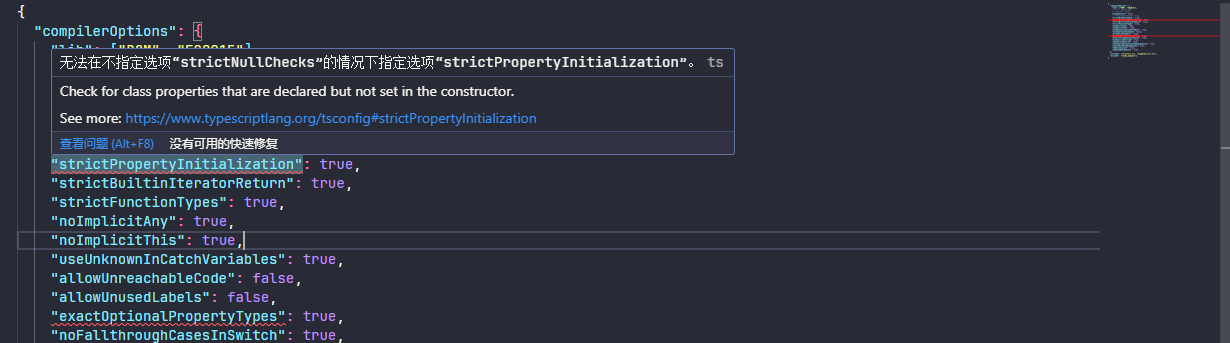
strictPropertyInitialization 和 exactOptionalPropertyTypes 配置项需要先指定 strictNullChecks 的配置,否则配置不生效
2.2、代码内核心配置
2.2.1、lib
TypeScript 包括一组内置 JS API(如 Math)的默认类型定义,以及浏览器环境中的事物(如 document )的类型定义。TypeScript 还包括与您指定的 target 匹配的较新 JS 功能的 API,更新详细配置可以参考 https://www.typescriptlang.org/tsconfig/#lib
当 lib 只设置以下时,当代码中使用到 document API 和 ES6 以上的新特性API 就会提示错误
{
"compilerOptions": {
"lib": ["ES2015"]
},
}
2.2.2、target
target 选项指定编译后的 JavaScript 版本,可以设置的值有 es3、es5、es6/es2015、es2016、es2017、es2018、es2019、es2020、es2021、es2022、es2023、es2024、esnext
2.2.3、module
module 指定编译后的所运行环境的模块系统,设置的值可以为 none、commonjs、amd、umd、system、es6/es2015、es2020、es2022、esnext、node16、node18、node20、nodenext、preserve
其中 commonjs、amd、umd、system、分别表示各自的模块系统。es6/es2015 表示 ESM 模块系统,es2020 除了 es6/es2015 的基本功能外,es2020 还增加了对 dynamic import and import.meta 而 es2022 进一步增加了对 top level await 的支持
node16 支持 ES Modules (ESM) 和 CommonJS (CJS) 两种模块系统。在 Node.js 16 中,你可以通过在 package.json 中设置 "type": "module" 来启用 ESM,或者在文件扩展名上使用 .mjs 来明确表示文件为 ESM。默认情况下,如果未设置 "type" 或文件扩展名为 .cjs,则 Node.js 使用 CommonJS
而 node18 和 node20 同样支持 ESM 和 CJS ,并且在模块方面进行了进一步的优化和改进而已。
exnext 和 nodenext 表示默认启用下个稳定版本
2.2.4、moduleResolution
指定模块解析策略,可以允许的值为 classic、node10/node、node16、nodenext、bundler
如果 module 选项设置为 commonjs,则 moduleResolution 应该设置为 node10 和 node 作用是一样的,仅支持用于 v10 之前的 Node.js 版本,只支持 CommonJS 模块
如果 module 选项设置为 node16、node18 和 node20,则 moduleResolution 应该设置为 Node16
如果 module 选项设置为 nodenext,则 moduleResolution 应该设置为 nodenext
如果 module 选项设置为 preserve 或 es2015 或更高版本,则 moduleResolution 应该设置为 bundler 否则则为 classic
2.2.5、baseUrl和path
{
"baseUrl": ".", // 设置一个基本目录
"paths": {
// 配置别名路径
"@/*": ["src/*"]
}
}import { add } from '@/utils/math';2.2.6、importHelpers
importHelpers 选项主要和 tslib 配合起来使用,当 target 选项设置为 es5 时,但是在代码中会用到 async 和 await 相关语法。tsc 进行编译时会处理兼容性 "importHelpers": true,
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5", // 指定编译后的 JavaScript 版本
"lib": ["DOM", "ES2024"],
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts", "globals.d.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}实际的使用代码
const getAPI = async (url: string) => {
// Get API
return {};
};当 importHelpers 不使用时,进行编译时查看结果
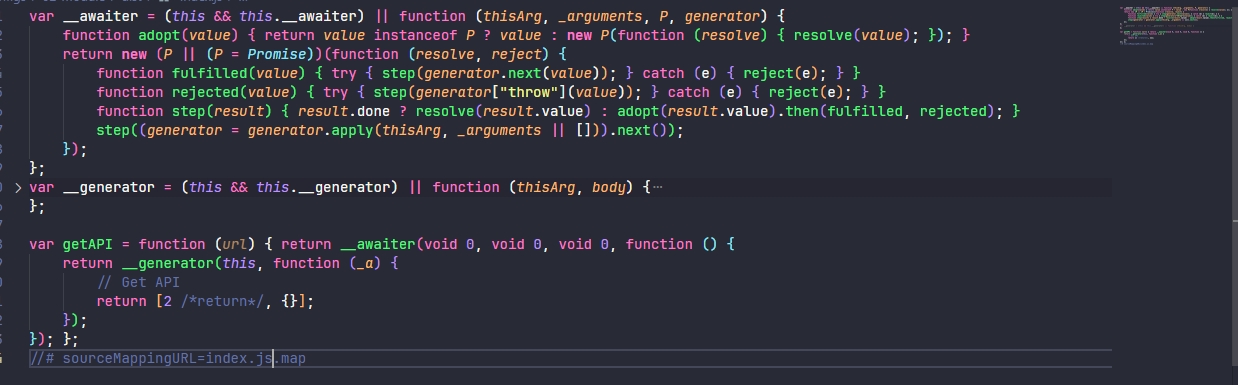
当 importHelpers 启用时,会提示需要按照 tslib
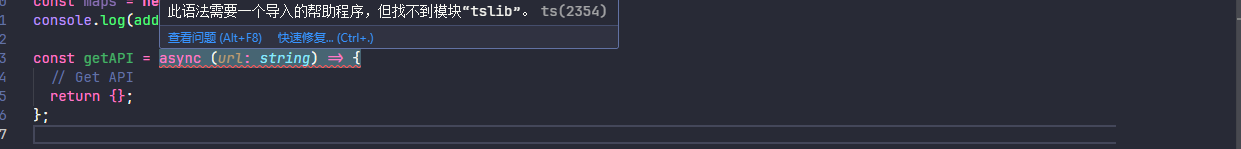
然后需要安装 tslib,并且 tslib 是运行时使用,使用 --save 进行安装
npm i tslib --save然后再次编译,其中 __awaiter 和 __generator 会从 tslib 辅助函数中进行导入
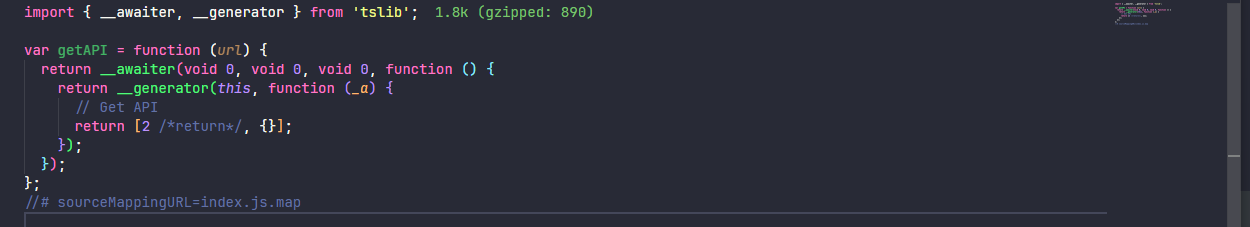
与该选项相关的配置为 noEmitHelpers ,主要就是取消对 tslib 帮助程序的使用,详细见:https://www.typescriptlang.org/tsconfig/#noEmitHelpers。
2.2.7、esModuleInterop 和 allowSyntheticDefaultImports
默认情况下(esModuleInterop 为 false 或未设置)TypeScript 将 CommonJS/AMD/UMD 模块视为 ES6 模块。
当 module 选项设置为 node16、nodenext、preserve 时,esModuleInterop 默认开启 true,否则则为 false
当 esModuleInterop 选项启动时默认也会启用 allowSyntheticDefaultImports 选项
allowSyntheticDefaultImports 选项则是允许合成默认导入
这里先配置以下设置
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5", // 指定编译后的 JavaScript 版本
"lib": ["DOM", "ES2024"],
"outDir": "dist",
"module": "commonjs", // 指定编译后的所运行环境的模块系统,不会开启 esModuleInterop
"moduleResolution": "node10"
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}在实际代码上,会提示模块 "node:fs" 没有默认导出。
import fs from 'node:fs';
fs.copyFile('', '', () => {});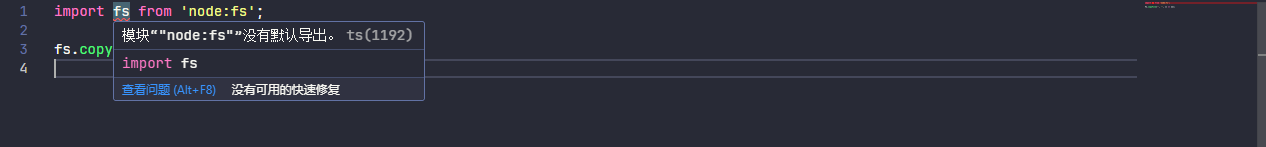
原因是 fs 模块是 CommonJS 方案实现,没有默认导出,此时有两个方案
第一种是通过以下方式进行解决
import * as fs from 'node:fs';
fs.copyFile('', '', () => {});
console.log('执行');编译后的代码依然可以执行
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
var fs = require("node:fs");
fs.copyFile('', '', function () { });
console.log('执行');第二种是通过 esModuleInterop,但是这一边我先不开启 esModuleInterop,先设置启用 allowSyntheticDefaultImports
{
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true
}Typescript 并不会报告错误
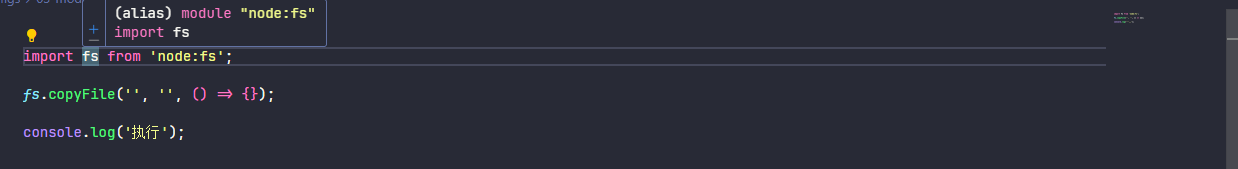
allowSyntheticDefaultImports 会在编译后的模块添加 default 属性,tsc 虽然可以编译成功但是编译后的代码无法执行
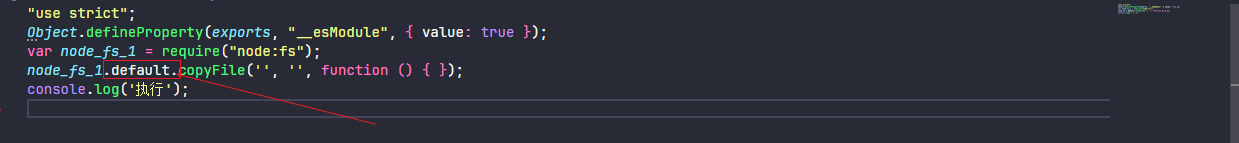
当在设置 esModuleInterop 时,编译之后会多出 __importDefault 辅助函数,并且编译后的代码可以执行
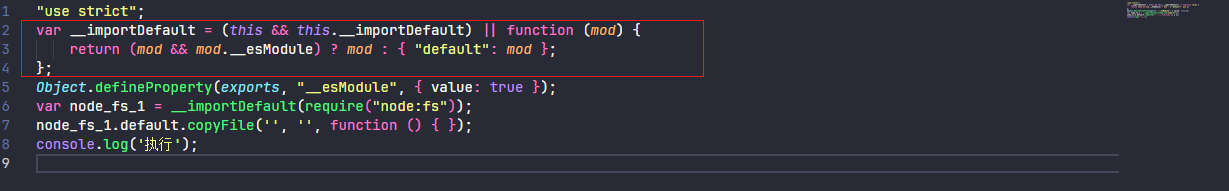
当设置 esModuleInterop 并且还使用以下方式还会多出其他辅助函数
import * as fs from 'node:fs';
fs.copyFile('', '', () => {});
console.log('执行');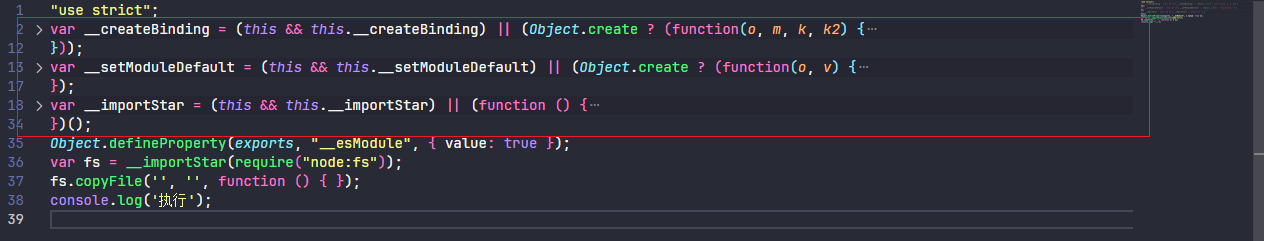
当 module 选项设置为以下设置时
{
"module": "es2022", // 指定编译后的所运行环境的模块系统
"moduleResolution": "bundler",
}
// 或
{
"module": "node16", // 指定编译后的所运行环境的模块系统,会默认开启 esModuleInterop allowSyntheticDefaultImports
"moduleResolution": "node16",
}当前代码中 无论使用以下那种方式都正常编译
import * as fs from 'node:fs';
// or
import fs from 'node:fs';2.3、jsx 相关设置
控制 JSX 构造在 JavaScript 文件中的发布方式。这仅影响以 .tsx 文件开始的 JS 文件的输出。
示例如下
export const HelloWorld = () => <h1>Hello world</h1>;当 jsx 设置 react-jsx 时,编译之后
import { jsx as _jsx } from "react/jsx-runtime";
export const HelloWorld = () => _jsx("h1", { children: "Hello world" });当 jsx 设置 react-jsxdev 时,编译之后
import { jsxDEV as _jsxDEV } from "react/jsx-dev-runtime";
const _jsxFileName = "/home/runner/work/TypeScript-Website/TypeScript-Website/packages/typescriptlang-org/index.tsx";
export const HelloWorld = () => _jsxDEV("h1", { children: "Hello world" }, void 0, false, { fileName: _jsxFileName, lineNumber: 9, columnNumber: 32 }, this);当 jsx 设置 preserve 时,编译之后
import React from 'react';
export const HelloWorld = () => <h1>Hello world</h1>;当 jsx 设置 react-native 时,编译之后
import React from 'react';
export const HelloWorld = () => <h1>Hello world</h1>;当 jsx 设置 react 时,编译之后
import React from 'react';
export const HelloWorld = () => React.createElement("h1", null, "Hello world");2.4、其他相关配置
2.4.1、outFile
如果 module 是 system 或 amd,则所有模块文件也将在所有全局内容之后连接到此文件中。
🔔注意:除非 module 为 None、System 或 AMD,否则不能使用 outFile。此选项不能用于 CommonJS 或 ES6 模块。
2.4.2、是否启用装饰器
{
"compilerOptions": {
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
},
}2.4.3、其他相关常用配置
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5", // 指定编译后的 JavaScript 版本
"lib": ["DOM", "ES2024"],
"outDir": "dist", // 文件输出目录
"preserveConstEnums": true, // 是否禁止删除枚举常量生成代码中的声明,默认为 false
"skipLibCheck": true, // 跳过类型声明文件的检查
"declaration": true, // 是否为每个 Typescript 文件生成 .d.ts 文件
"declarationDir": "./types", // 将生成的 .d.ts 指定目录
"noEmit": false, // 不输入编译后的文件
"noEmitOnError": false, // 若 Typescript 报告了任何错误就不会输出编译后的文件
"sourceMap": true, // 开启 sourceMap
"removeComments": false, // 是否移除注释
"allowJs": true, // 是否对js文件进行编译,默认:false
"checkJs": false // 是否检查js代码是否符合语法规范,当使用checkJs,必须使用allowJs,默认:false
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts", "globals.d.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}